Multithreading
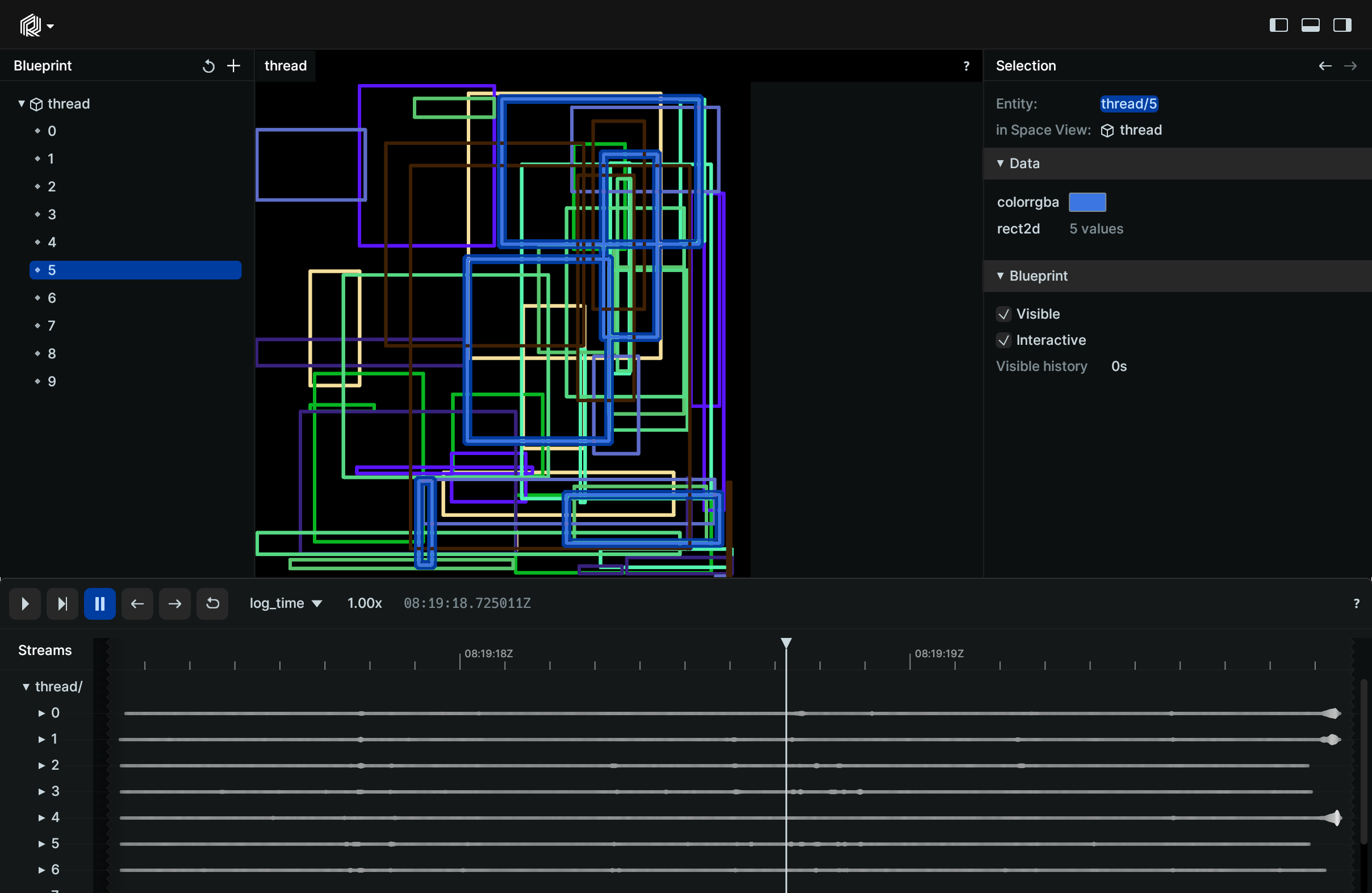
Demonstration of logging to Rerun from multiple threads.
Used Rerun types used-rerun-types
Logging and visualizing with Rerun logging-and-visualizing-with-rerun
This example showcases logging from multiple threads, starting with the definition of the function for logging, the rect_logger, followed by typical usage of Python's threading module in the main function.
def rect_logger(path: str, color: npt.NDArray[np.float32]) -> None:
for _ in range(1000):
rects_xy = np.random.rand(5, 2) * 1024
rects_wh = np.random.rand(5, 2) * (1024 - rects_xy + 1)
rects = np.hstack((rects_xy, rects_wh))
rr.log(path, rr.Boxes2D(array=rects, array_format=rr.Box2DFormat.XYWH, colors=color)) # Log the rectangles using RerunThe main function manages the multiple threads for logging data to the Rerun viewer.
def main() -> None:
# … existing code …
threads = []
for i in range(10): # Create 10 threads to run the rect_logger function with different paths and colors.
t = threading.Thread(target=rect_logger, args=(f"thread/{i}", [random.randrange(255) for _ in range(3)]))
t.start()
threads.append(t)
for t in threads: # Wait for all threads to complete before proceeding.
t.join()
# … existing code …Run the code run-the-code
To run this example, make sure you have the Rerun repository checked out and the latest SDK installed:
pip install --upgrade rerun-sdk # install the latest Rerun SDK
git clone git@github.com:rerun-io/rerun.git # Clone the repository
cd rerun
git checkout latest # Check out the commit matching the latest SDK releaseInstall the necessary libraries specified in the requirements file:
pip install -e examples/python/multithreadingTo experiment with the provided example, simply execute the main Python script:
python -m multithreading # run the exampleIf you wish to customize it, explore additional features, or save it use the CLI with the --help option for guidance:
python -m multithreading --help